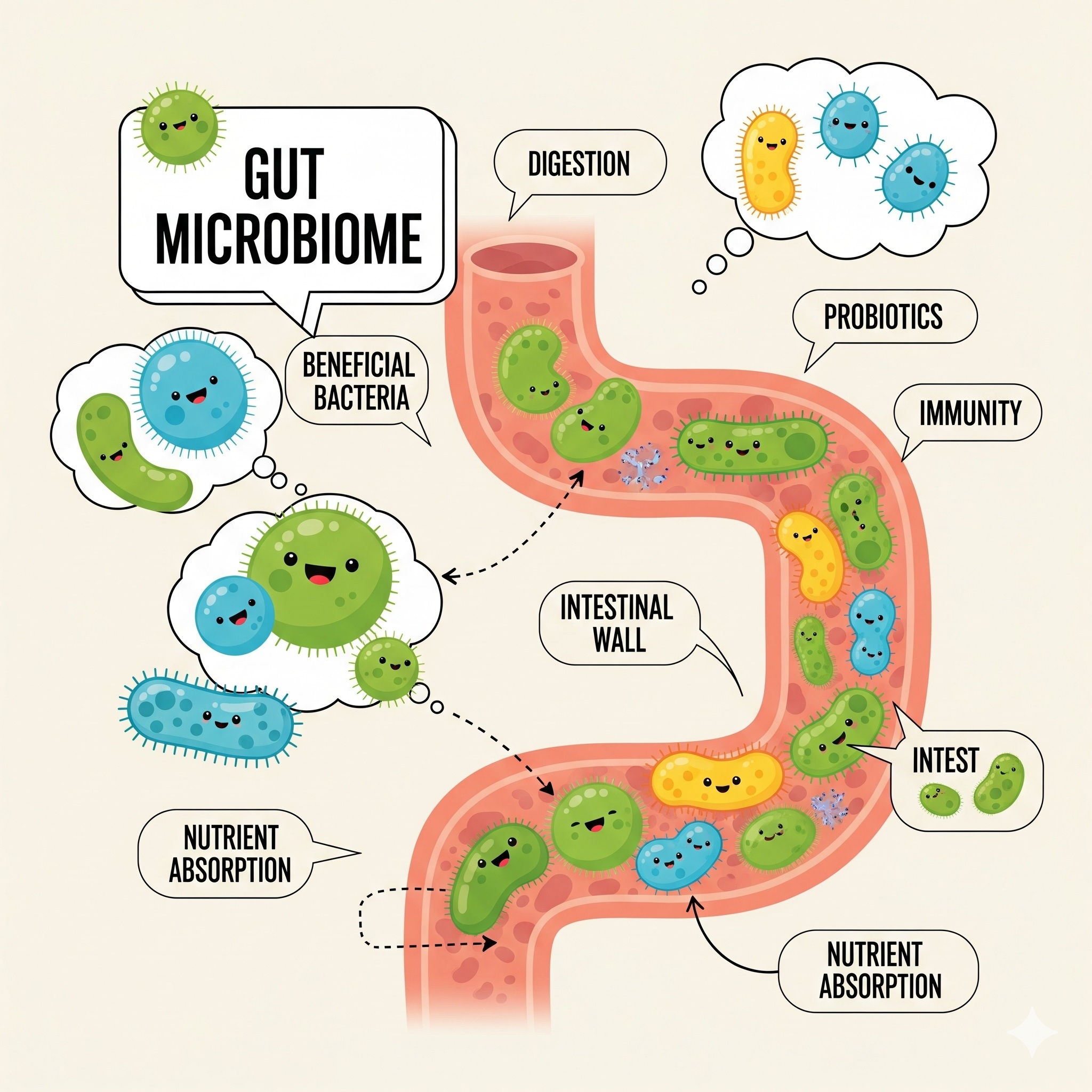
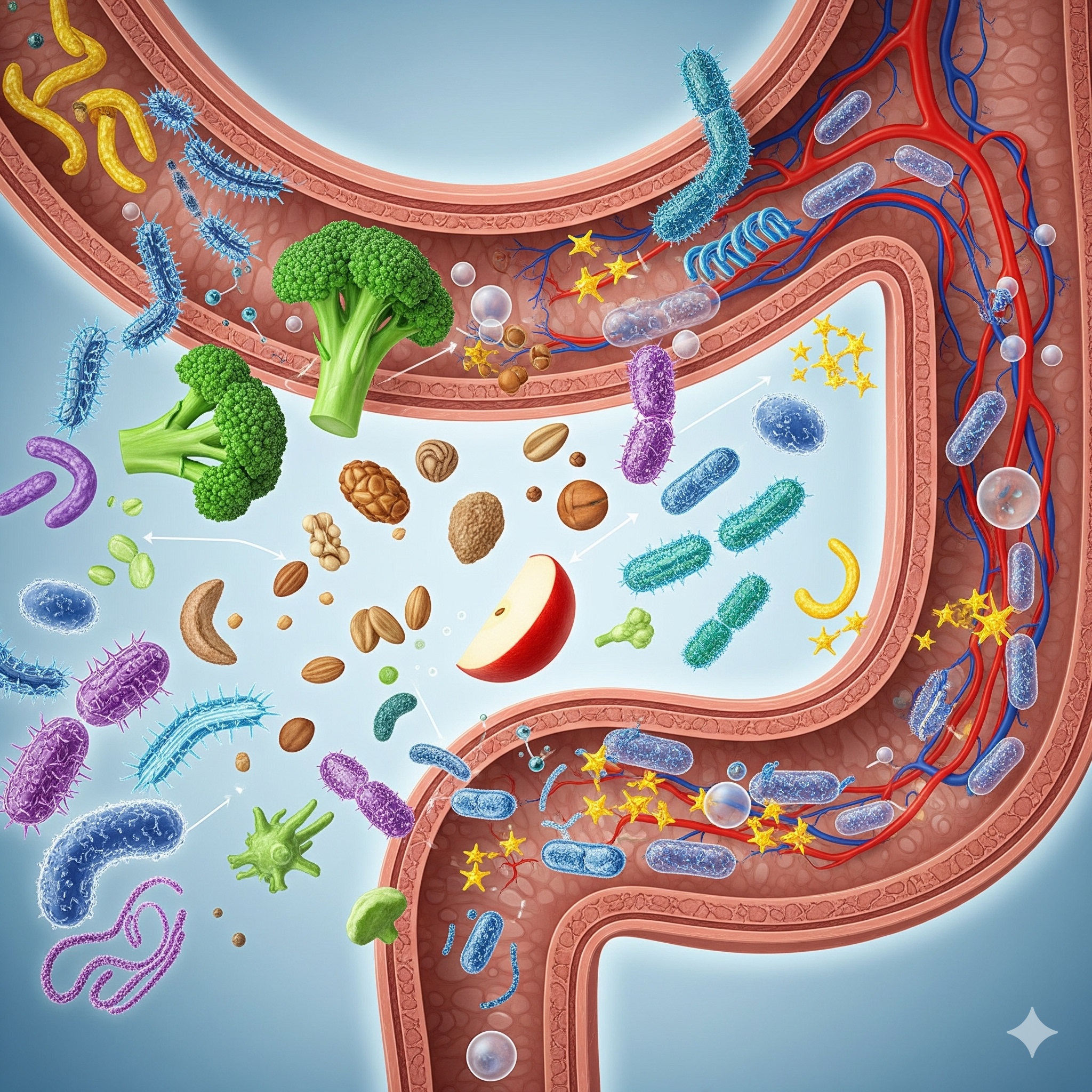
The human body functions as a complex network of organs, systems, and processes that work together to keep us alive and thriving. At the center of this intricate system lies the digestive system, which not only digests food but also contributes significantly to overall well-being. The concept of gut health has become a major focus in medical research, as scientists now understand that the gut does far more than we ever imagined.
In this blog, we will dive deep into what gut health means, why it matters for your daily life, and how to maintain a healthy gut for lasting gut wellness.
What Does Gut Health Mean?
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms—bacteria, fungi, and viruses—living in the gastrointestinal tract. This internal ecosystem is often called the gut microbiome. A diverse and well-balanced microbiome helps the body digest food efficiently, absorb nutrients, and protect against harmful pathogens.
When your gut is balanced, it supports not only your digestive system but also your immune function, energy levels, and even mental health. Poor gut health, on the other hand, can lead to chronic inflammation, food intolerances, fatigue, and a range of other health issues.
Why Gut Health Matters
You may think of your gut as only responsible for digesting food, but its influence goes far beyond that. Here are the key reasons why gut wellness is crucial for overall health:
1. Gut Health and Immunity
Did you know that nearly 70% of your immune system resides in the gut? A healthy gut trains your immune system to distinguish between harmful invaders and harmless substances. Poor gut health increases susceptibility to infections, autoimmune conditions, and allergies.
2. Gut-Brain Connection
The gut and the brain communicate through the gut-brain axis. This two-way communication means your mood, stress levels, and mental clarity are directly influenced by your microbiome. Beneficial gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which regulate mood and sleep.
3. Metabolism and Weight Management
Your digestive system plays a direct role in metabolism. An imbalanced gut can extract calories differently, sometimes leading to weight gain. People with diverse gut bacteria often find it easier to maintain or lose weight compared to those with less diversity.
4. Chronic Inflammation and Disease Prevention
An unhealthy gut often leads to chronic inflammation—a root cause of conditions like diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, and certain cancers. Maintaining gut wellness reduces inflammation and lowers the risk of these diseases.
Signs of Poor Gut Health
If you are wondering whether your gut is out of balance, here are some common symptoms:
- Persistent bloating and gas.
- Irregular bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea).
- Frequent fatigue or brain fog.
- Skin issues like acne, eczema, or rashes.
- Weakened immunity and frequent illnesses.
- Unexplained mood swings, anxiety, or depression.
These signs indicate that your digestive system may need care and attention.
How to Improve Gut Health
Achieving a healthy gut requires conscious effort in daily lifestyle and dietary habits. Below are proven strategies to boost your microbiome and ensure long-term gut wellness.
1. Eat a Fiber-Rich Diet
Dietary fiber fuels beneficial gut bacteria. Whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes encourage microbial diversity, which is essential for gut balance.
2. Add Fermented Foods
Foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut are rich in probiotics—live bacteria that restore gut balance. These foods directly enhance gut health.
3. Limit Processed Foods and Sugar
Junk food and refined sugar feed harmful bacteria and yeast. Reducing processed foods creates space for beneficial bacteria to thrive.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water supports digestion, nutrient absorption, and the integrity of the intestinal lining. Proper hydration is a cornerstone of gut wellness.
5. Manage Stress
Stress alters the gut-brain axis and negatively affects microbial composition. Meditation, yoga, breathing exercises, and physical activity help maintain gut balance.
6. Get Quality Sleep
Poor sleep weakens immunity and disrupts gut bacteria. Aim for 7–9 hours of restorative sleep to support a healthy gut.
7. Use Probiotics and Prebiotics
- Probiotics: live bacteria that replenish your microbiome (found in supplements and fermented foods).
- Prebiotics: dietary fibers that feed beneficial bacteria (found in garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus).
Together, they create an environment for long-term gut wellness.
Lifestyle Habits for Better Gut Wellness
Diet is not the only factor—your lifestyle habits also shape your microbiome. Consider the following practices:
- Exercise regularly to promote microbial diversity.
- Avoid overuse of antibiotics unless medically necessary.
- Limit alcohol intake to prevent irritation of the gut lining.
- Quit smoking to protect both immunity and gut balance.
These small yet consistent lifestyle changes significantly improve the health of your digestive system.
Gut Health Across Life Stages
Gut health changes over time:
- Infants develop their microbiome through birth, breastfeeding, and early diet.
- Adults maintain balance through nutrition, stress control, and exercise.
- Older adults often experience reduced microbial diversity, making probiotics and fiber-rich foods critical.
Recognizing these changes ensures you support your gut wellness at every age.
The Future of Gut Health Research
Modern science is uncovering groundbreaking insights into the microbiome. Researchers are exploring personalized nutrition based on microbiome testing and studying the potential of probiotics as treatments for conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), depression, and obesity.
This evolving field highlights just how important gut health is for the future of healthcare.
Conclusion: Why Gut Health Should Be Your Priority
Your gut is not just about digestion—it is the foundation of health. A well-balanced microbiome strengthens immunity, boosts mood, regulates weight, and protects against chronic disease. By making small yet consistent choices—such as eating fiber-rich foods, adding probiotics, staying hydrated, and managing stress—you can cultivate a healthy gut and ensure long-term gut wellness.
In short: better health truly begins with the gut.