Did you know that a large portion of your immune system actually lives inside your gut? Modern science has revealed that gut health and immunity are deeply connected. When your gut is balanced, your immune defenses are strong and responsive. When your gut is imbalanced, you may be more susceptible to infections, allergies, and chronic inflammation.
This article explores how gut immunity works, why a healthy gut is essential for whole-body protection, and practical ways to support your immune system naturally — including the role of probiotics.
Why the Gut Is the “Headquarters” of Immunity
Around 70% of immune cells are located in the gastrointestinal tract. This isn’t a coincidence — the gut is the first line of defense against the outside world. Every bite of food introduces new microbes and potential pathogens. Your gut lining and microbiome work together to:
- Identify harmful bacteria, viruses, and toxins
- Trigger immune responses when necessary
- Prevent overreactions to harmless substances (like food proteins)
In short, a healthy gut is your immune system’s training ground.
Understanding Gut Immunity
The Gut Microbiome’s Role
The gut microbiome is a community of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that live in your digestive tract. These microbes help:
- Maintain a strong intestinal barrier
- Regulate inflammation
- Produce antimicrobial substances that keep harmful invaders in check
- Communicate with immune cells to “teach” them tolerance
A balanced microbiome leads to immune resilience. When the microbiome becomes imbalanced — a state called dysbiosis — the immune system may overreact, leading to chronic inflammation, allergies, or autoimmune problems.
The Gut Barrier
The gut lining acts like a filter, letting nutrients pass into the bloodstream while blocking harmful substances. A compromised gut barrier (sometimes called “leaky gut”) can let unwanted particles through, triggering immune activation and systemic inflammation.
Signs Your Gut-Immune Connection May Be Struggling
Because the gut plays such a central role in immunity, poor gut health can manifest in surprising ways:
- Frequent colds or infections
- Chronic bloating, gas, or irregular digestion
- Skin issues (eczema, psoriasis, acne)
- Seasonal allergies or food intolerances
- Autoimmune flare-ups
- Fatigue or brain fog
If you experience several of these symptoms regularly, supporting your gut may improve immune function.
How to Support a Healthy Gut for Stronger Immunity
The good news: you can improve gut immunity through diet and lifestyle. Here’s how:
1. Eat a Diverse, Plant-Rich Diet
Variety is key. Different gut bacteria thrive on different fibers. Include:
- Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, spinach
- Fruits: berries, bananas, apples
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, barley
- Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas
These foods feed beneficial bacteria (prebiotics), helping them flourish.
2. Add Probiotics
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that help restore balance to the gut microbiome. Good sources include:
- Yogurt with live cultures
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Tempeh and miso
Probiotic supplements may also be helpful, especially after antibiotic use.
3. Reduce Processed Foods and Sugar
Highly processed foods and excess sugar can feed harmful bacteria and yeast, tipping the microbiome out of balance. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress suppresses immunity and disrupts gut function. Support your gut-brain connection with:
- Meditation or mindfulness
- Gentle exercise like yoga or walking
- Breathing techniques
5. Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is when your immune system repairs and resets. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night to keep your gut and immune system in sync.
6. Stay Active
Moderate, regular exercise improves microbial diversity and supports circulation of immune cells throughout the body.
The Role of Probiotics in Immune Health
Research shows that probiotics may:
- Reduce the duration and severity of common colds
- Support the production of antibodies
- Decrease inflammation in the gut
- Help regulate immune responses in allergies and autoimmune conditions
Not all probiotics are the same — look for well-studied strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium lactis for immune support.
Gut Health and Autoimmunity
When the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, autoimmune conditions develop. While genetics play a role, many researchers believe an unhealthy gut can trigger immune dysregulation. Supporting gut health may help reduce flare-ups or severity in conditions like:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
When to See a Professional
If you have chronic digestive discomfort, persistent infections, or autoimmune symptoms, consult a qualified healthcare professional. They may recommend stool testing, microbiome analysis, or targeted treatment to restore gut balance.
Key Takeaways
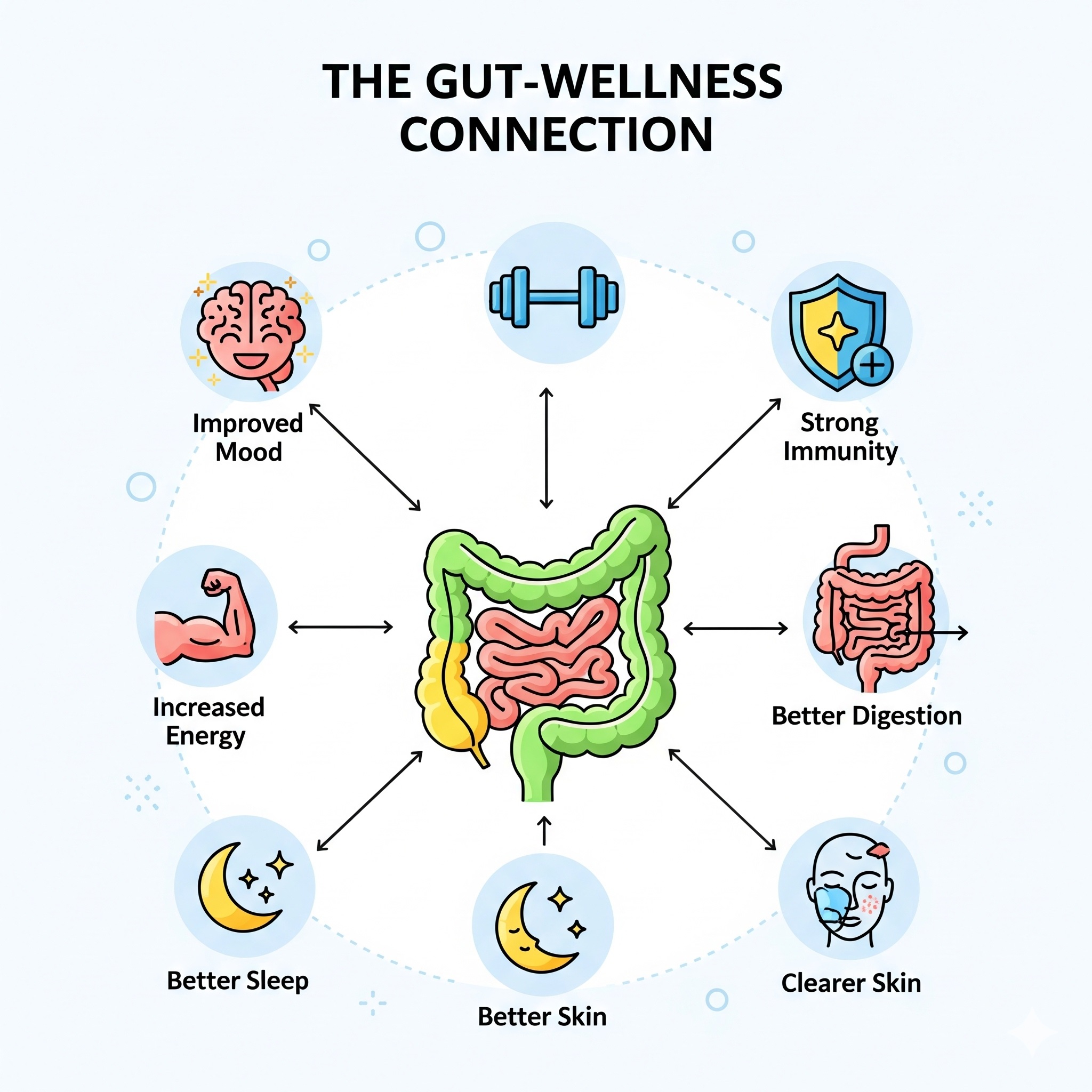
- Gut immunity is a cornerstone of health — 70% of your immune system is in the gut.
- A healthy gut helps regulate inflammation, fight pathogens, and prevent overactive immune responses.
- Probiotics, fiber-rich foods, stress management, and sleep all support gut-immune balance.
Your gut is not just a digestive organ — it’s a powerful immune ally. By nurturing your microbiome, you strengthen your defenses and improve your overall well-being.